Collaborative filtering is a method of making automatic predictions about the preference of a consumer by collecting preferential information from various users. The underlying assumption of this approach is that if consumer A shares the same opinion as consumer B on an issue, A is more likely to share the opinion of B on a different issue than other randomly chosen consumer.
All tagged Excel
Discrete Choice Analysis and Price Optimization with Excel
Unlike conjoint analysis that requires consumers to rank the level of each product attribute, discrete choice analysis need not to do that. Conjoint analysis uses multiple linear regression whereas discrete choice analysis adopts logistic regression, using maximum likelihood estimation and the logit model to estimate the ranking of product attributes for the population represented by the sample.
Price Bundling with Excel
Today we’ll be building this model using a sample dataset mobilecarrier.xls, it gives the amount 77 representative are willing to pay per month for each service. The key to this model is to set up a spreadsheet that tells me, for any set of prices for each possible product combination, how much revenue we can obtain from this sample of customers. Then we’ll will use the Solver plug-in to determine the set of prices for the product combinations that maximizes the revenue.
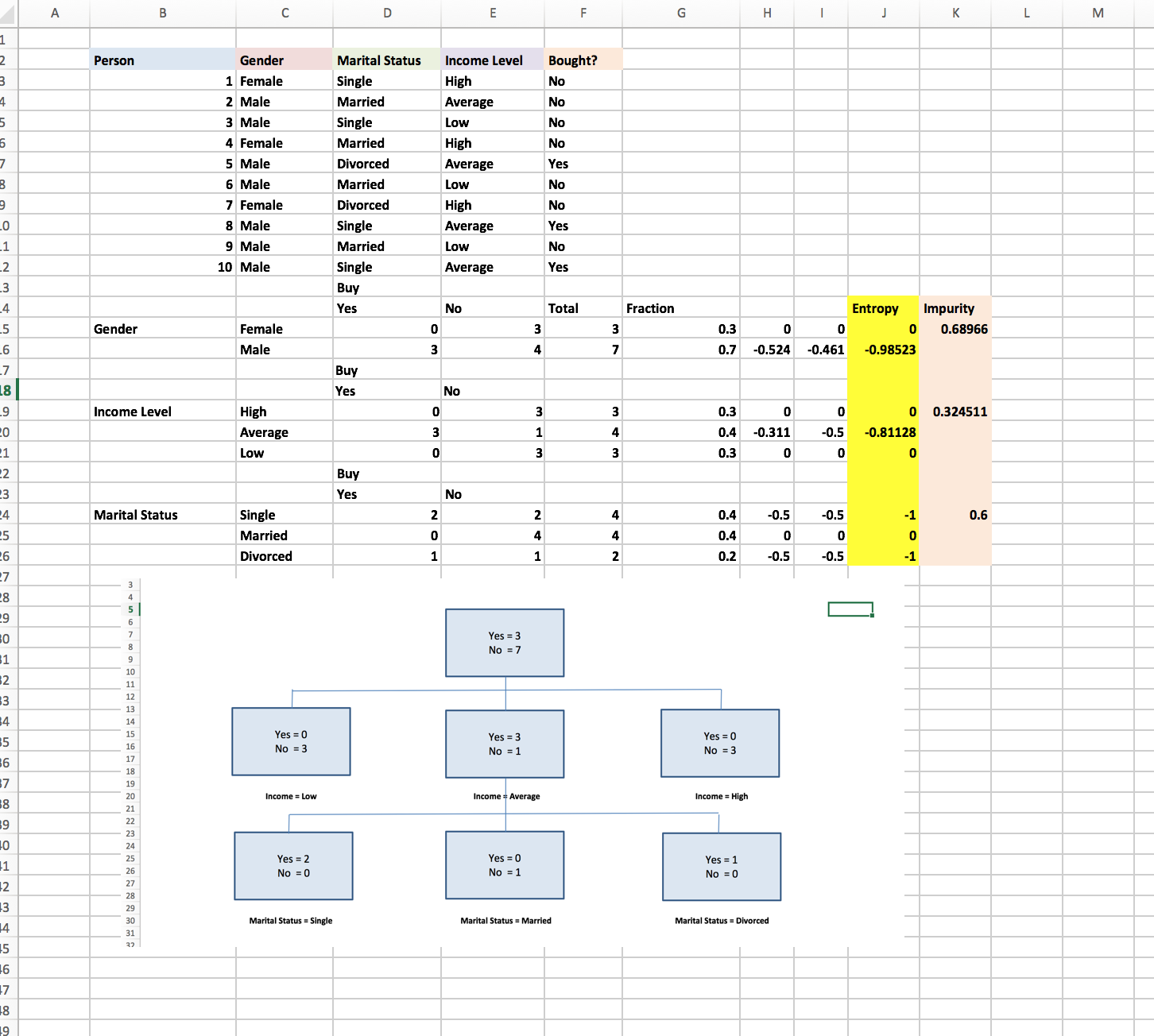
Classification Trees for Segmentation with Excel
There are many metrics to used to measure the impurity of a node. Here we’ll be using the concept of entropy to measure the impurity of a node. To compute for each attribute value category level combination, we will need the equation: P(i|X=a)*Log2(P(i|X=a) combined with IFERROR to ensure that when P(i|X=a)=0 Log2(0) the undefined value will be replaced by zero. In here, we use the formula =IFERROR((D15/$F15)*LOG(D15/$F15,2),0).
Market Simulator: Conjoint Analysis with Excel
Conjoint analysis enables analyst to determine the product characteristics that drive a consumer’s preference for products. Through conjoint analysis, analyst will be able to learn the relative importance of the product attributes and within each attribute the ranking of the levels.
Market Basket Analysis and Lift
Lift is the most commonly used tool in market basket analysis. The lift for a combination of purchase products and/or day of week is defined by this equation: (The actual number of times combination occurs) divided by (Predicted number of times combination occurs if items in combination were independent).
Multiplicative Model: Trend and Seasonality with Excel
To accurately forecast sales when the data has seasonality and trends, we’ll need to identify and separate them from the data series. Sometimes it is as simple as using moving averages to smooth data and eliminate seasonality (e.g. excel scatter plot with trend line. When monthly seasonal influence is suspected, use a 12-month moving average, when analyzing trend in quarterly data, use a four-quarter moving average). Yet, sometimes it is more complicated than that.
Calculating Customer Lifetime Value with Excel
There is no one correct way to build a customer life time value model, or actually any models. Today I’ll build the model base off the method created by Gupta and Lehman to calculate the customer value multiplier. Their method utilizes discount and retention rates to forecast a customer’s long-term value denoted by multiplier. A multiplier of three means that the customer’s long term value is three times the profit he generates during the first period.